- Home
- Sustainability
- Environment
- Climate Change
Climate Change
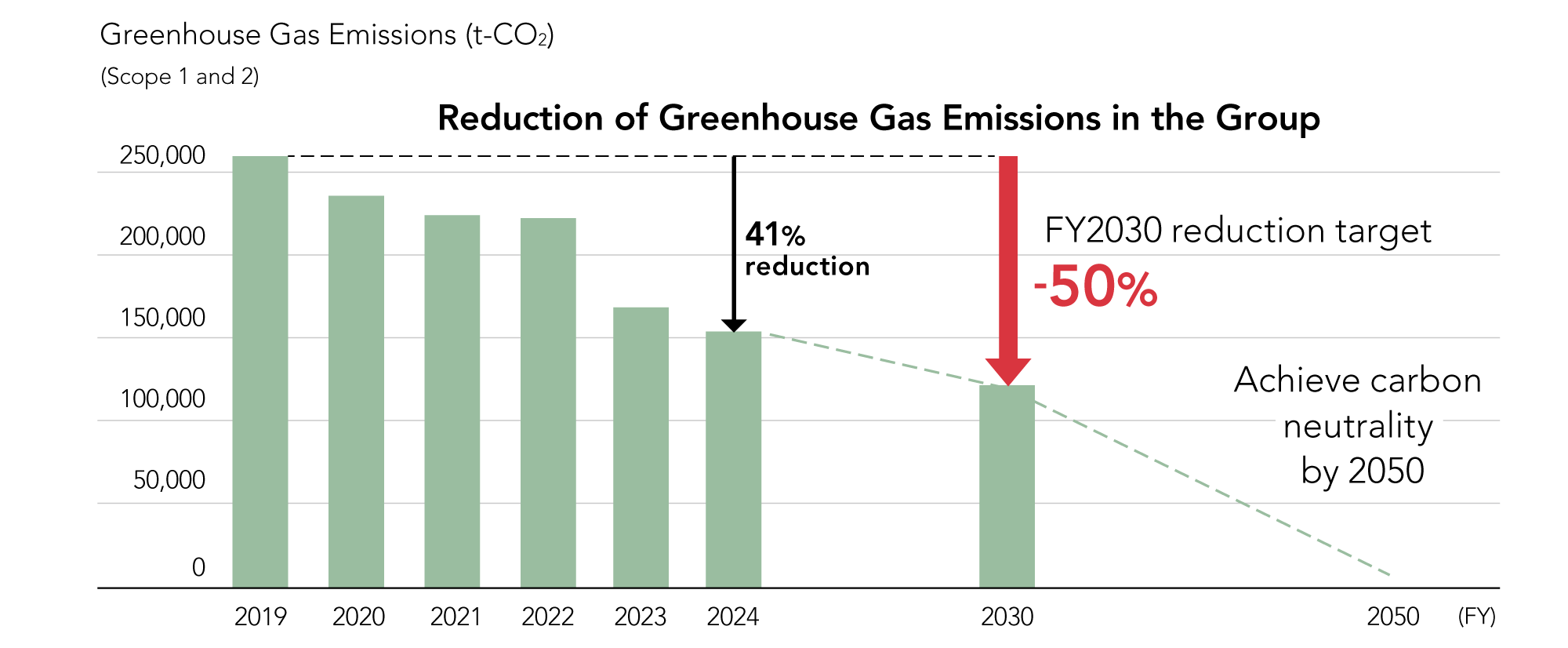
We recognize that climate change can lead to the depletion of forest resources, as well as increased risks associated with global warming and potential financial burdens. In addition, we view reducing greenhouse gas emissions across the entire supply chain as a corporate responsibility and have identified “climate change” as a material issue. Our response to climate change has focused mainly on the Paper Manufacturing & Processing segment, where greenhouse gas emissions are high. We have promoted energy efficiency and the utilization of non-fossil energy sources to reduce emissions. In fiscal 2024, two companies in the containerboard manufacturing business switched to renewable energy derived from hydroelectric power, and they also took measures such as upgrading to energy-saving facilities and improving productivity. At Japan Pulp & Paper as well, we offset all of our Scope 2 emissions by purchasing Non-Fossil Certificates, helping the group achieve a reduction rate of about 41% from the reference year. Based on greenhouse gas reduction targets set in May 2024, the group will proactively drive forward initiatives to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050.
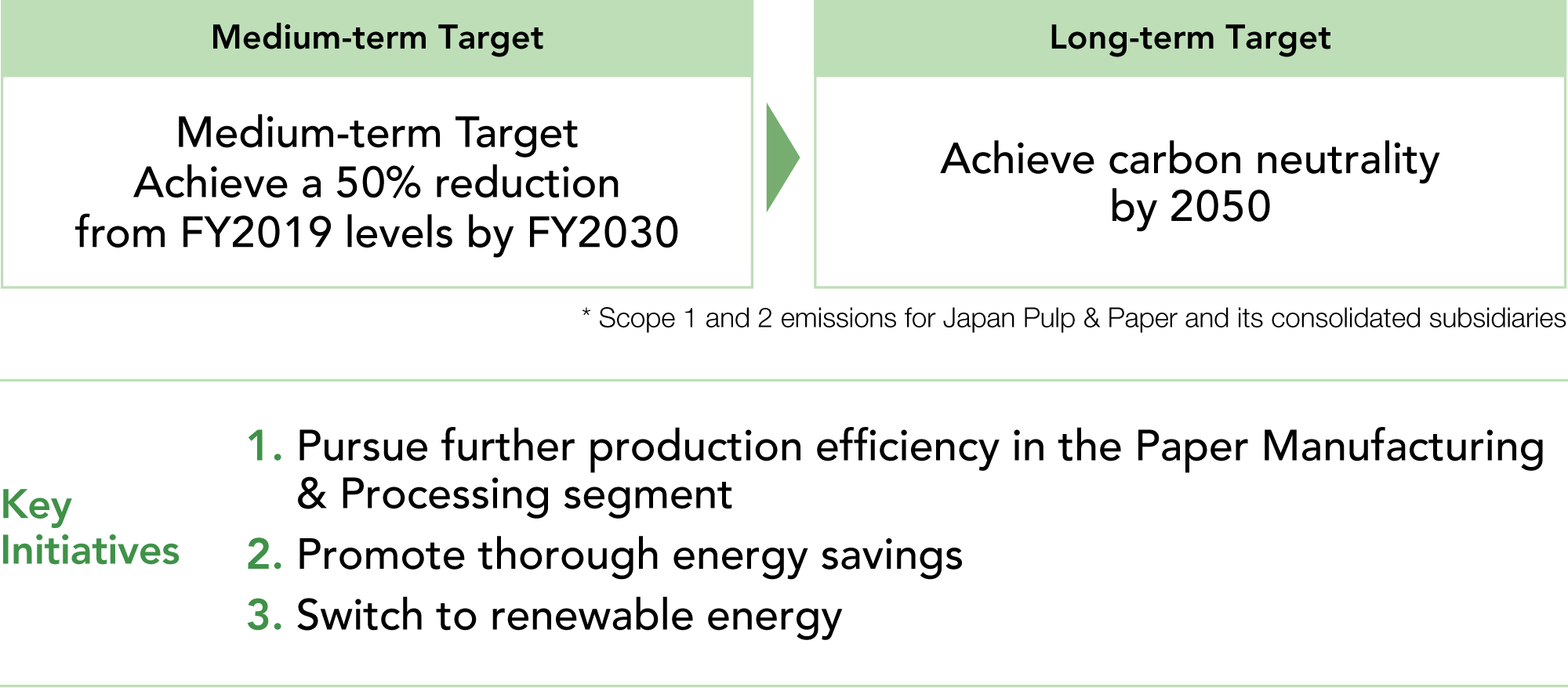
Japan Pulp & Paper Group Medium- and Long-term Reduction Targets
for Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Disclosure Based on TCFD Recommendations
The group recognizes that responding to climate change is an urgent issue. We have endorsed the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) recommendations and joined the TCFD Consortium. We have also conducted scenario analyses of the risks and opportunities that climate change poses to the group’s businesses, including the Paper and Paperboard Wholesaling, Paper Manufacturing & Processing, Raw Materials & Environment, and Real Estate Leasing segments.* We disclose information on governance, strategy, risk management, and metrics and targets as recommended by the TCFD.
Based on our Environmental Policy, we will work harder to address climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and will promptly disclose relevant information.
- While there are five business segments (Japan Wholesaling, Non-Japan Wholesaling, Paper Manufacturing & Processing, Raw Materials & Environment, and Real Estate Leasing), the Japan Wholesaling and Non-Japan Wholesaling segments were treated as the Paper and Paperboard Wholesaling segment for the scenario analysis.
What is the TCFD?

The Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) was established by the Financial Stability Board to study climate-related information disclosure and how financial institutions should respond. Climate change, a global issue, is becoming a factor that has a serious impact on corporations, and is turning into either a risk or an opportunity for mid- to long-term business activities. Under these circumstances, it has become necessary for companies to incorporate the climate change factor into their business strategies in order to achieve sustainable growth. The final TCFD report recommends that companies assess the financial impact of climate change risks and opportunities on their operations and disclose them in four areas: governance, strategy, risk management, and metrics and targets.
What is the TCFD Consortium?

The TCFD Consortium is a group of companies and financial institutions that support the TCFD. It was established in Japan to discuss effective corporate information disclosure and how to use disclosed information to help financial institutions make appropriate investment decisions.
1. Governance
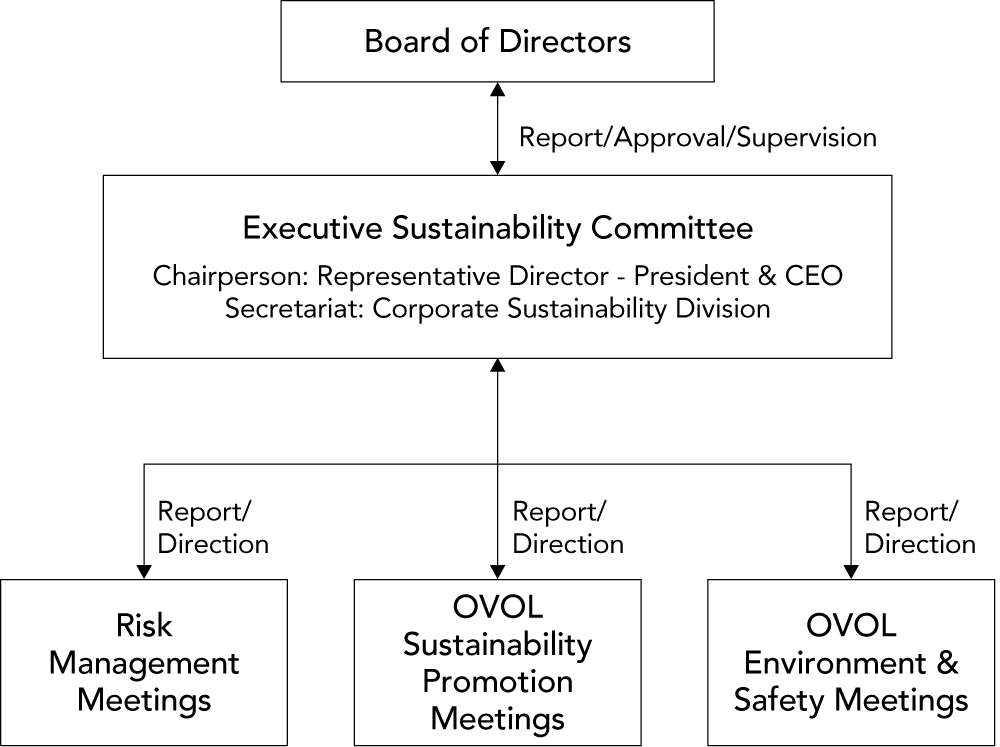
We established the Executive Sustainability Committee to promote sustainable business management in a more proactive way. Under the supervision of the Board of Directors, the Executive Sustainability Committee is responsible for formulating policy and planning strategy on all climate change-related matters for the entire group, as well as overseeing the process of finding solutions to ESG issues and meeting our ESG goals. The committee also analyzes the group’s risks and opportunities and studies countermeasures in line with the TCFD recommendations. The Executive Sustainability Committee is chaired by the representative director-president, who has ultimate responsibility for management decisions related to climate change. The progress of matters reviewed and discussed by the committee is regularly reported to the Board of Directors, and important matters are resolved by the board.
Sustainability and Governance Structure
2. Strategies (Risks, Opportunities, and Responses)
The group has identified risks and opportunities associated with climate change in four business segments: the Paper and Paperboard Wholesaling business, Paper Manufacturing & Processing, Raw Materials & Environment, and Real Estate Leasing, using two scenarios developed by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), the International Energy Agency (IEA), and other specialist organizations: one in which the increase in average temperature is limited to 1.5°C (2.0°C in some scenarios) and another in which the average temperature increase exceeds 4°C. Risks and opportunities posed by climate change are categorized by risks and physical impacts associated with the transition to a low-carbon society. In order to incorporate these risks and opportunities into our business strategy, we conducted an assessment of the associated financial impacts from the short-term, medium-term, and long-term perspectives.
Risks and Opportunities
| Category | Impact on the Group | Countermeasures | Scale of Impact | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risks | Transition | Policies and Regulations | Significant increase in operating costs in the paper manufacturing business due to increased carbon taxes |
|
Large |
| Reputation | Decline in corporate value and loss of stakeholder confidence due to delays in response to climate change, resulting in lower sales revenues, impact on financing ability, and decline in brand value |
|
Moderate | ||
| Physical | Acute | Extensive damage to sites, facilities, inventories, real estate, etc., due to wind and flood damage |
|
Moderate | |
| Suspension of business due to disruptions in the supply chain caused by wind and flood damage, and resulting decline in sales revenues |
|
Moderate | |||
| Chronic | Impact of storm surge and other flood damage on coastal sites due to rise in sea levels |
|
Moderate | ||
| Opportunities | Market | Contribution to business performance from increased demand for functional materials related to electronic components associated with the advance of electrification |
|
Moderate | |
| Contribution to business performance from increased demand for environmentally friendly products such as paper with FSC® and PEFC Forest Certification and recycled paper |
|
Moderate | |||
| Contribution to business performance from increased demand for paper products due to move away from plastics |
|
Moderate | |||
- Scale of Impact is categorized as “Large” if the event in question poses a risk to the survival of the business and “Moderate” if a major change in the business strategy is required.
- Scale of Impact (Large, Moderate) were compiled based on “Applying Enterprise Risk Management to Environmental, Social and Governance-related Risks,” COSO & WBCSD.
Financial Impact Analysis
Based on the financial impact scenario analysis, we expect that the introduction of a carbon tax would have a significant impact, particularly on the group’s paper manufacturing business. On the other hand, we believe that we can lower that impact by reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
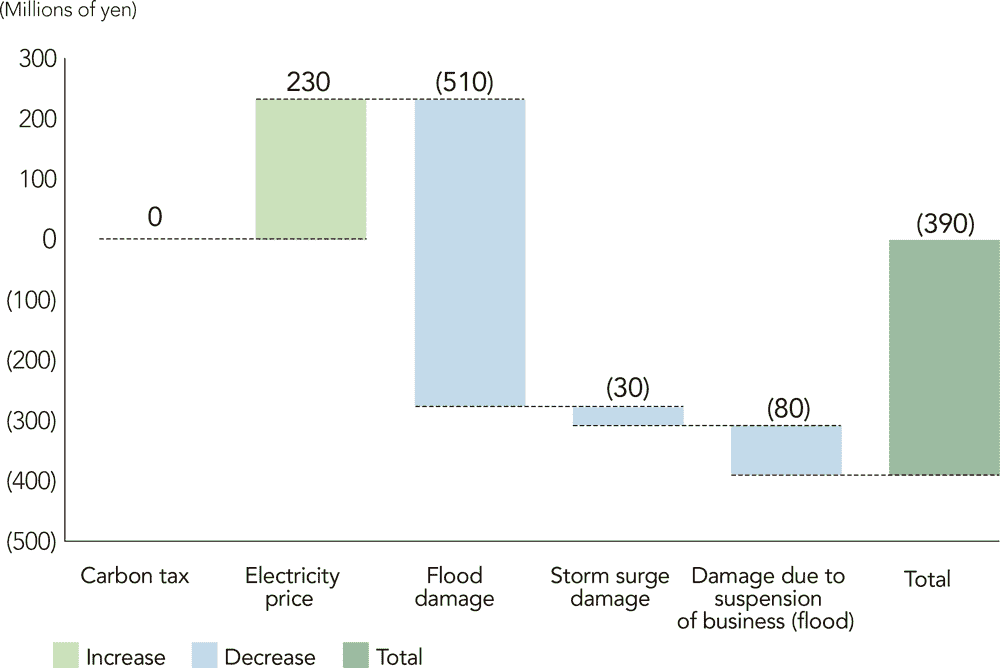
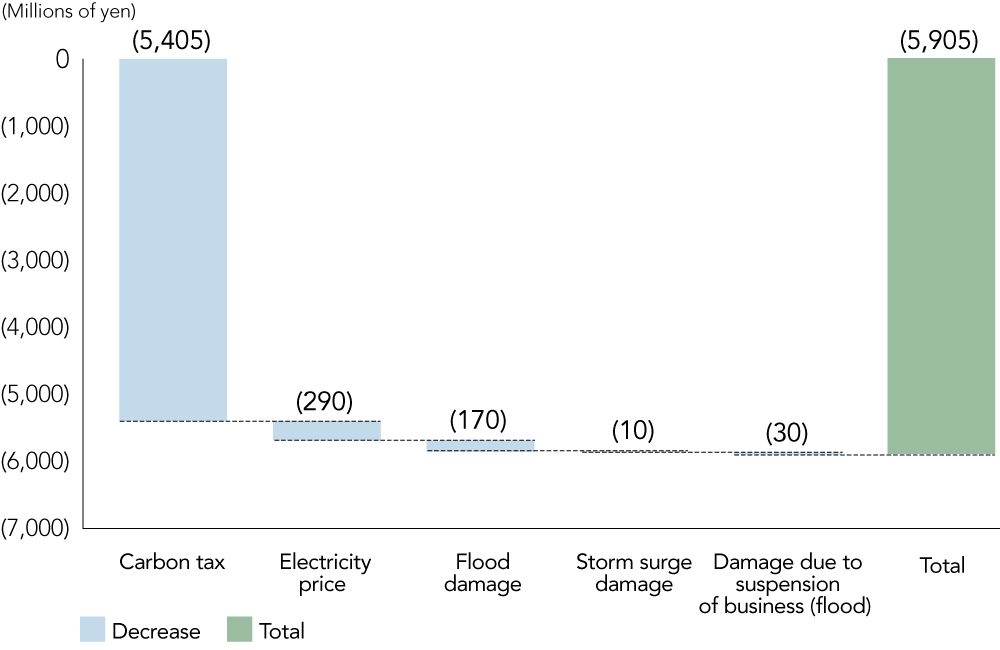
In terms of physical risks, we estimate that damage to the main bases of the group in Japan due to abnormal weather events such as floods and typhoons would be in the range of JPY 200 million to JPY 600 million in the 1.5°C (2°C) and 4°C scenarios respectively. In the event of severe damage to a business partner, there is a possibility that factories in the supply chain would not be able to operate and that the transportation of products, raw materials, and fuel would be disrupted, resulting in damage beyond our estimate.
Analysis Results *1
| Item | Risks | Analysis Content | Financial Impact (2050) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4°C Scenario | 1.5°C (2°C) Scenario | |||
| Carbon tax | Transition Risk | Impact of carbon tax introduction | - | JPY (5,405) million *2 |
| Electricity price | Transition Risk | Impact of electricity price changes | JPY 230 million | JPY (290) million |
| Flood damage | Physical Risk | Annual average flood damage | JPY (510) million | JPY (170) million |
| Storm surge damage | Physical Risk | Annual average storm surge damage | JPY (30) million | JPY (10) million |
| Damage due to suspension of business (flood) | Physical Risk | Annual average damage due to suspension of business (flood) | JPY (80) million | JPY (30) million |
- Analysis of Japan Pulp & Paper Co., Ltd. and consolidated subsidiaries in Japan
- Analysis based on greenhouse gas emissions in 2024
Referenced Scenarios
| Transition Risks | IEA NZE | Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario (NZE) This scenario assumes that net zero CO2 emissions will be achieved by 2050. |
|---|---|---|
| IEA SDS | Sustainable Development Scenario (SDS) In this scenario, the path to achieving the goal set in the Paris Agreement to “hold the increase in the global average temperature to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels and pursue efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels” was analyzed. |
|
| IEA APS | Announced Pledges Scenario (APS) This scenario reflects the ambitions and targets of each member country to reduce emissions, assuming that all the announced pledges of each government are implemented (also includes those that have not yet been implemented). |
|
| IEA STEPS | Stated Policies Scenario(STEPS) This scenario incorporates the current plans of each government, including policy initiatives that have already been announced and implemented around the world. |
|
| IEA B2DS | Beyond 2 Degrees Scenario (B2DS) This scenario assumes there is a 50% probability that the temperature rise in 2060 does not exceed 1.75°C. |
|
| Physical Risks | IPCC RCP2.6 | A scenario that projects a temperature increase of around 2°C compared with pre-industrial levels |
| IPCC RCP8.5 | 4°C scenario with the highest temperature increase |
Parameters Used for Financial Impact Analysis
| Item Name | Standard | Unit | Present | 2050 | Source | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4℃ | 2℃ | 1.5℃ | |||||
| Carbon Price | Developed countries (With net zero pledge) |
USD/t-CO2 | 0 | 0 | 200 | 250 | IEA WEO 2022 |
| Electricity Price | Japan | USD/MWh | 216 (2018) |
203 (2040) ※ |
232 (2040) ※ |
- | IEA WEO 2019 |
| Flood Rate | Japan | - | - | 4 (2040) ※ |
2 (2040) ※ |
- | Proposal for Flood Control Plans Based on Climate Change (Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism) |
| Storm Surge Rate | Japan | - | - | 2 | 1.2 | - | Assessment Report on Climate Change Impacts in Japan (Ministry of the Environment) |
- Analysis of figures for 2040 as there are no parameters for 2050
Financial Impact (Risk) under the 4°C Scenario (2050)
Financial Impact (Risk) under the 1.5°C (2°C) Scenario (2050)
3. Risk Management
The Executive Sustainability Committee identifies risks and opportunities related to climate change for the group as a whole, formulates response plans, instructs corresponding organizations led by the Corporate Sustainability Division, manages progress of measures, and reports to the Board of Directors. The Board of Directors approves the content of reports or gives instructions on improvements, and monitors results to ensure that appropriate risk management is being implemented. Risk matters related to climate change deliberated by the Executive Sustainability Committee are directed to the Risk Management Meetings, the OVOL Sustainability Promotion Meetings, and the OVOL Environment & Safety Meetings, and reflected in the group’s overall risk management.
4. Metrics and Targets
In response to climate change, we have set “Japan Pulp & Paper Group Medium- and Long-term Reduction Targets for Greenhouse Gas Emissions” that aim to achieve a 50% reduction from fiscal 2019 levels by fiscal 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2050. To achieve the 2030 medium-term targets, we are currently implementing various measures to reduce Scope 1 and 2 emissions throughout the group, including switching our purchased electricity to renewable energy, and fundamentally reforming production efficiency through DX. In fiscal 2024, two companies in the containerboard manufacturing business switched their purchased electricity to renewable energy, and Japan Pulp & Paper Co., Ltd. also purchased Non-Fossil Certificates to offset its emissions. As a result, we reduced Scope 1 and 2 emissions by approximately 41% throughout the group, compared with fiscal 2019 levels. Every consolidated group company formulated greenhouse gas reduction targets and action plans, and is carrying out various policies and investments to achieve the 50% reduction target by fiscal 2030.
At Japan Pulp & Paper, we will work on formulating greenhouse gas reduction targets and reduction measures for Scope 3 emissions as part of our efforts to acquire Science Based Targets (SBT) certification.
[Related link]
Topics
Promotion of Solar Panel Installation at Worksites by Premier Paper Group
The U.K.’s Premier Paper Group, one of our group companies, is installing solar panels at its business sites as part of its sustainable management. The installation work is expected to be completed by the end of 2025. By transitioning to renewable energy, we aim to reduce environmental impact and contribute to the U.K.’s green economy.
This initiative forms the core of Premium Paper’s comprehensive sustainability strategy, as they seek to promote the responsible use of resources and minimization of environmental impact across the entire paper industry. The solar panels installed at the first five worksites are expected to generate about 547,500 kWh of electric power annually, reducing CO2 emissions by more than 257 tons every year.
Japan Pulp & Paper GmbH (Germany) Awarded Gold Medal in Sustainability Assessment by EcoVadis
Japan Pulp & Paper GmbH (Dusseldorf, Germany), one of our group companies, was awarded a gold medal in a 2023 sustainability assessment by EcoVadis.
EcoVadis is an international organization that assesses corporate initiatives related to ESG (environmental, social, and governance). The assessment is divided into the four themes of Environment, Labor and Human Rights, Ethics, and Sustainable Procurement.
Japan Pulp & Paper GmbH first won the bronze medal in 2022. By strengthening various sustainability-related initiatives, they won the silver medal in 2023 and improved results sufficiently to enter the top 5% of companies and win the gold medal in the most recent assessment.
Going forward, the Japan Pulp & Paper Group will continue to advance sustainability initiatives with the aim of conducting sustainable business activities and achieving both economic and social value.
Climate Change-Related Data
Energy Consumption
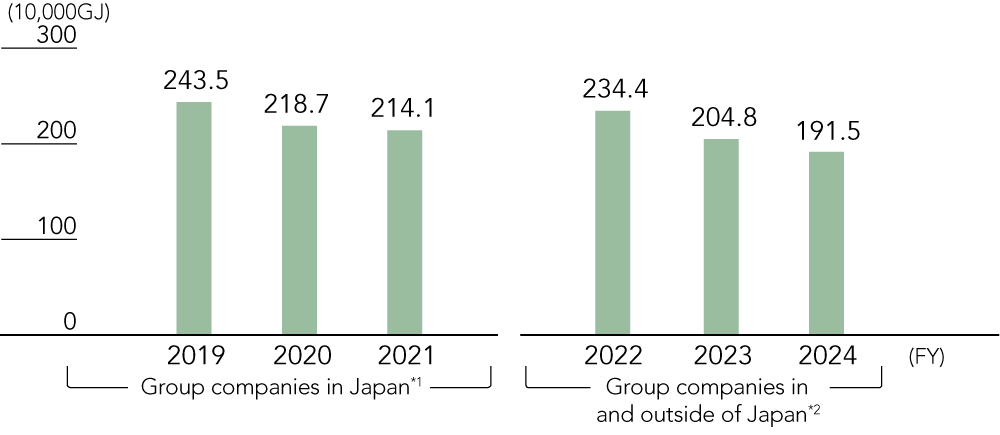
Electricity Consumption
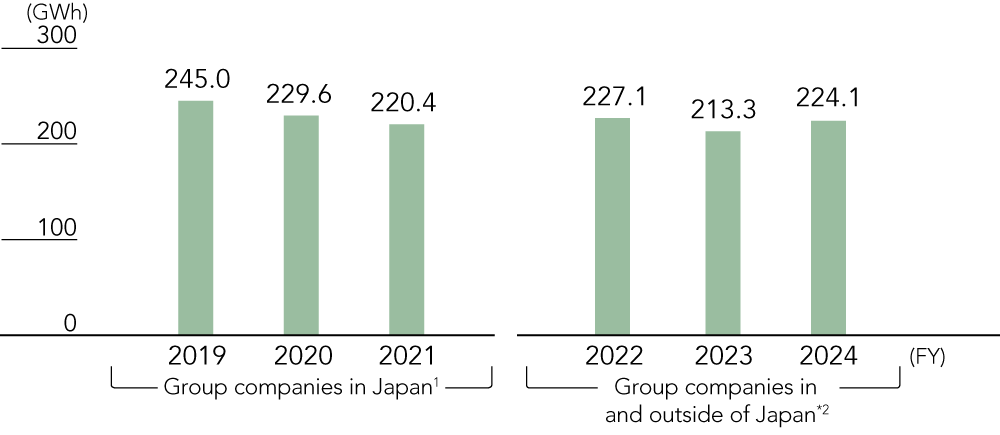
Greenhouse Gas Emissions *3,4,5,6
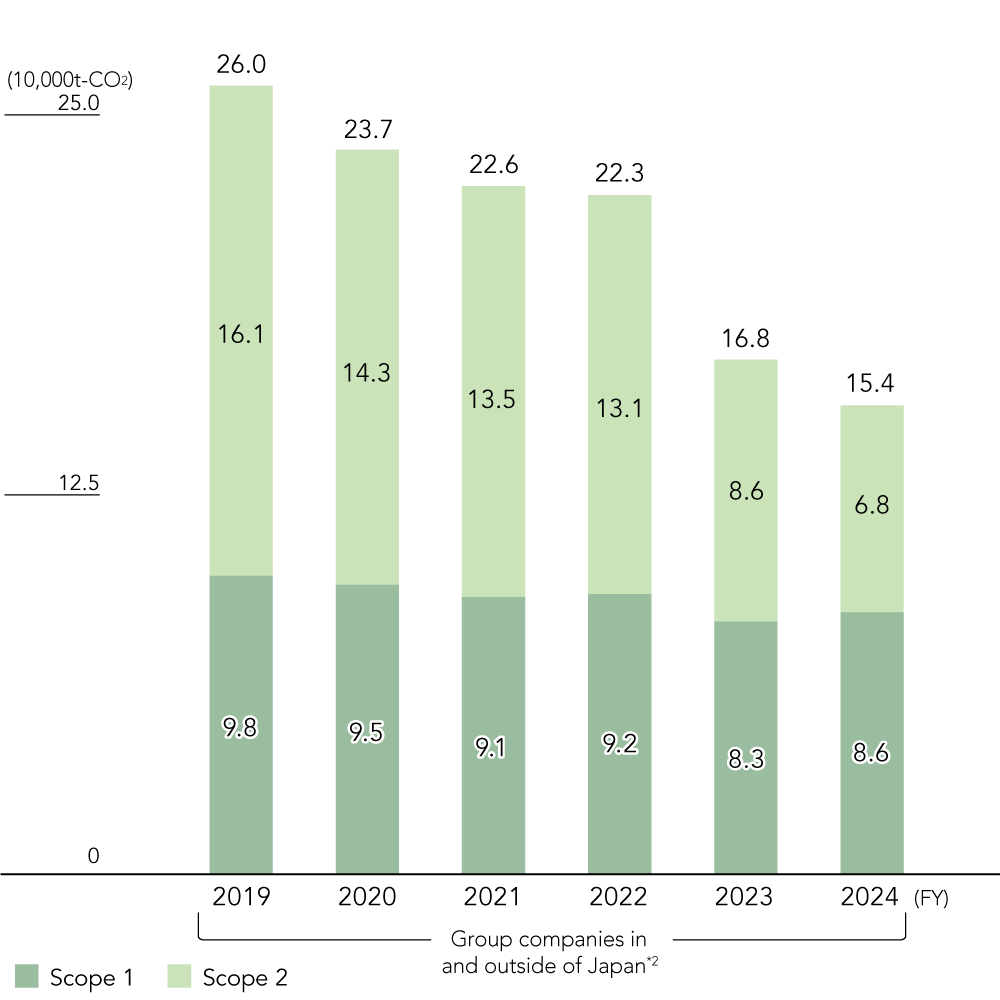
- Japan Pulp & Paper and consolidated subsidiaries in Japan
- Japan Pulp & Paper and consolidated subsidiaries in and outside of Japan
- Figures for subsidiaries outside of Japan for fiscal 2019 to 2021 are estimated based on 2022 emissions.
- Calculated in accordance with the standards of the GHG Protocol. The coefficients used for calculations are based on Japan’s Act on Promotion of Global Warming Countermeasures.
- Scope 1 and 2 GHG emissions have been recalculated retroactively to fiscal 2019 due to business acquisitions, etc.
- Third-party verification of Scope 1 and 2 GHG emissions for fiscal 2021 to 2023 and of Scope 3 for fiscal 2023 (parent company) has been conducted by the Japan Management Association GHG Certification Center.
Scope 3 Breakdown (Consolidated)
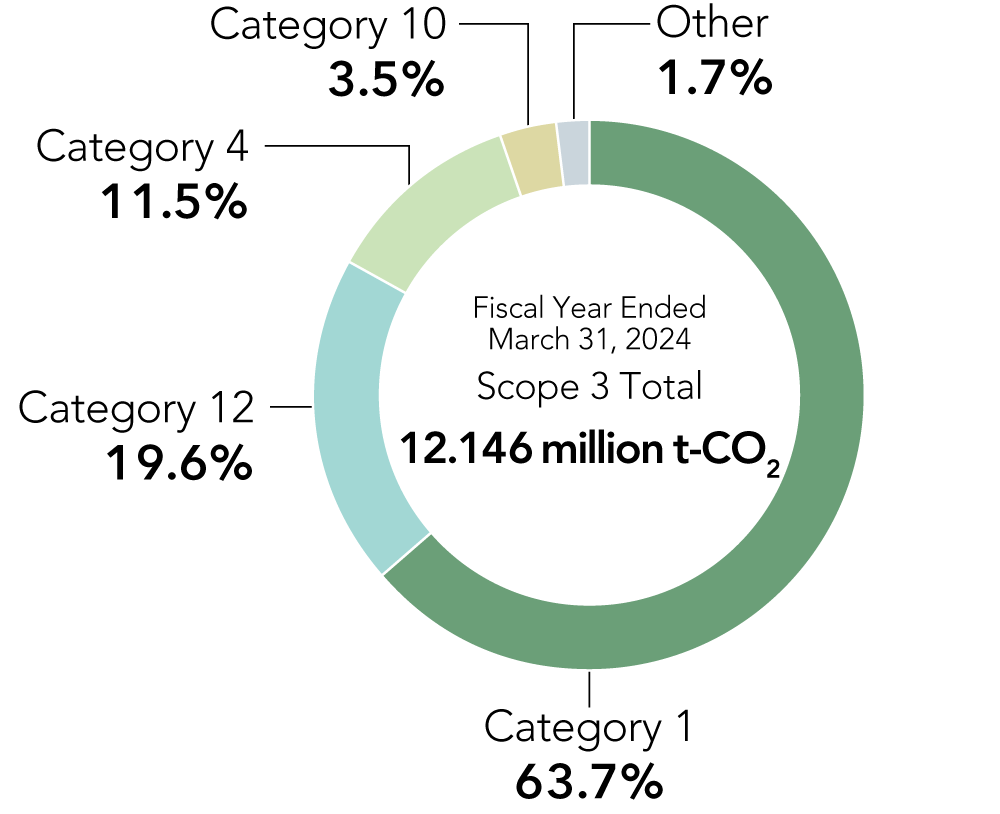
(Unit: 10,000 t-CO2)
| Item | Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2023 (10,000 t-CO2) |
Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2024 (10,000 t-CO2) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Purchased goods and services | 756.4 | 773.4 | |
| Capital goods | 1.4 | 1.2 | |
| Fuel- and energy-related activities | 2.4 | 3.6 | |
| Upstream transportation and distribution | 79.0 | 140.0 | |
| Waste generated in operations | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| Business travel | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| Employee commuting | 0.2 | 0.2 | |
| Upstream leased assets | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| Downstream transportation and distribution | 1.4 | 2.3 | |
| Processing of sold products | 42.2 | 42.5 | |
| Use of sold products | 0.1 | 11.6 | |
| End-of-life treatment of sold products | 47.9 | 237.8 | |
| Downstream leased assets | 2.0 | 2.0 | |
| Franchises | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| Investments | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| Scope 3 Total | 933.1 | 1,214.6 | |
- Calculation standard: Ministry of the Environment’s “Corporate Value Chain (Scope 3) Accounting and Reporting Standard” and “GHG Protocol: Technical Guidance for Calculating Scope 3 Emissions”
- Excluded categories: There are no relevant activities for categories 8, 14, and 15.